Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What is Agentic Process Automation
- 3 Business benefits APA offers?
- 4 What should executives know- Roadmap to navigate agentic automation
- 5 Key Use Cases in Agentic Process Automation
- 6 Best Practices for Implementing Agentic Process Automation
- 7 How to Implement Agentic Process Automation
- 8 Agentic Automation Trends in the Middle East
- 9 Conclusion
Introduction
Automation is evolving. No longer limited to scripted tasks or rule-based workflows. Agentic Process Automation(APA)—that integrates AI and business logic to enable systems to not just act, but decide, adapt, and collaborate.
This is a response to a critical need– modern businesses operate in real-time, and often complex environments.
APA bridges that gap by introducing intelligent agents which are autonomous, context-aware systems capable of interpreting goals, learning from data, adjusting to new inputs, and working alongside humans.
Today we will discuss APA, what should executives know and care about, use cases, best practices, and its business impact.
What is Agentic Process Automation
Agentic Process Automation uses software agents powered by large language models, GenAI, large action models (LAMs), workflow orchestration, and other advanced forms of AI.
These agents are capable of executing complex tasks without continuous human supervision— interacting with business applications, managing APIs, interpreting unstructured data across systems and teams.
Input data is an important part of Agentic Process Automation systems.
With machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) these systems make sense of real-time data, to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and make informed decisions that enable reduced reliance on manual oversight.
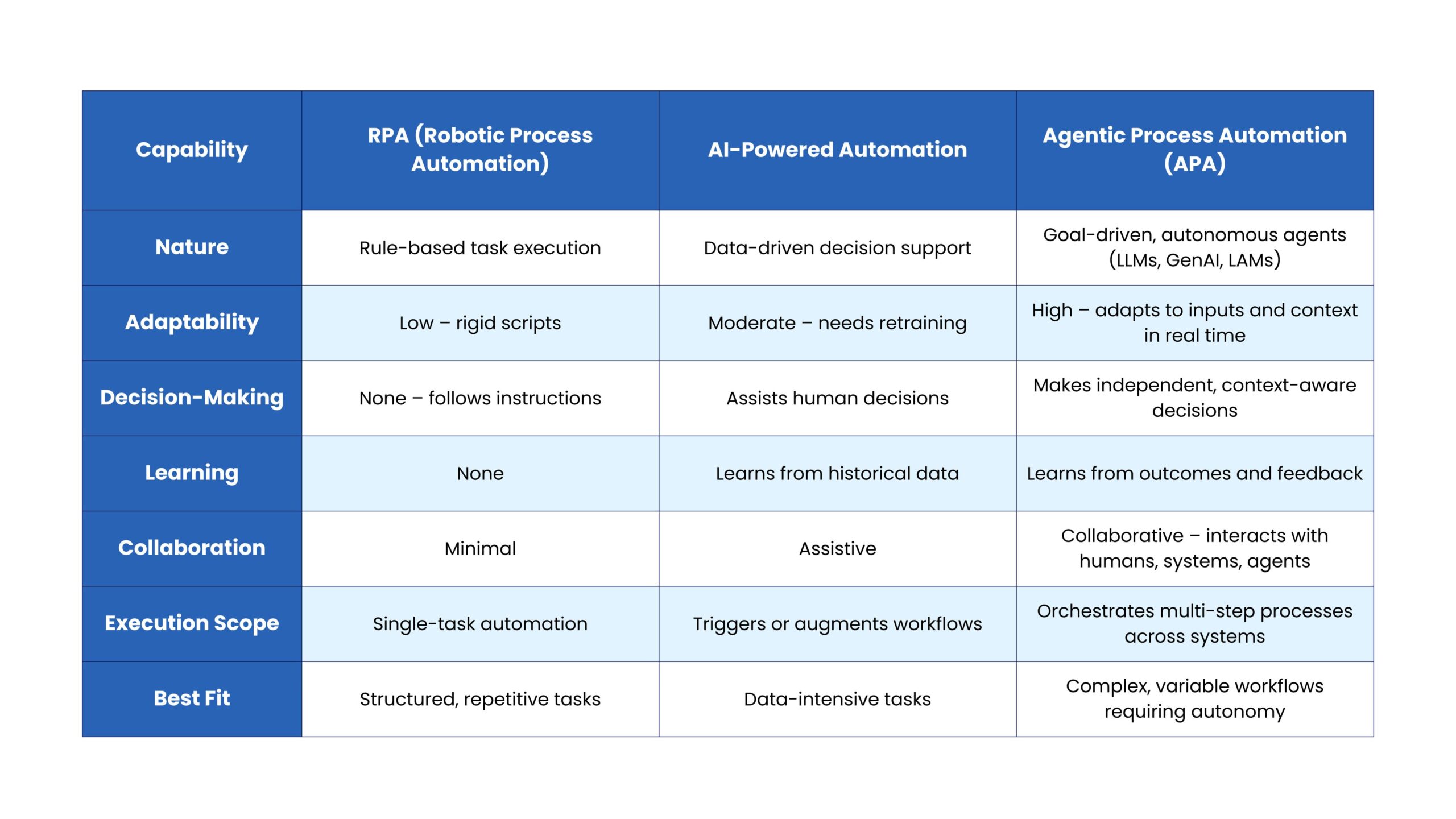
Unlike RPA which implements linear logic, APA supports dynamic environments and outcome-driven collaboration.
Also, agentic automation does not operate in isolation but integrates with existing automation tools, including RPA and traditional AI, forming a unified Intelligent Automation ecosystem that leverages the unique strengths of each technology.
Here is how agentic automation differs from RPA and intelligent automation-
Business benefits APA offers?
Agentic Process Automation enables software agents to autonomously manage complex processes which allows-
Expansion of business processes that can be automated
More efficiency and productivity
With RPA there are places in end-to-end processes that must be filled via manual human intervention.
Autonomous agents can handle probabilistic, less-well-structured tasks, allowing more processes to be fully automated end-to-end.
This results in high-performing, accurate automated processes on the one hand, and more time for people to focus productively on higher-impact work on the other.
Innovation and competitive advantage
AI agents’ ability to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make recommendations supports innovation.
The capability to autonomously carry out complex analyses can help identify ways to deliver better products & services quickly
Increased visibility in business processes and their impact
The ability of agentic automation to keep an eye on itself not only helps make processes better over time but also lets companies accurately figure out how much impact automation has and its ROI for both tasks and processes.
What should executives know- Roadmap to navigate agentic automation
Agentic automation is not an all-or-nothing approach— it exists on a spectrum of autonomy, and adaptability.
APA takes automation further by enabling goal-driven, self-improving agents and reduces friction by working alongside RPA, AI models, and workflow engines.
Understanding where it fits within your automation strategy is the first step.
Is APA Right for Your Business?
Determining whether Agentic Process Automation is the right fit for your business starts with assessing operational complexity.
If your workflows involve multi-layered processes requiring constant adaptation and intelligent decision-making, agentic automation is a high-value solution to consider.
Key factors to evaluate:
- Scalability & Workload Management: Agentic process automation can handle increasing workloads without adding manual overhead and autonomously optimizes processes as business needs evolve.
Unlike traditional automation, which scales linearly with scripts and rule updates. - Decision-Making Speed & Agility: In fast-paced industries, delays in decision-making can be costly. APA is suitable for sectors where real-time decisions are critical, such as- supply chain management, customer service, IT operations, etc.
- Adapting to changes: Businesses operating in volatile and regulated industries need automation that can respond to change without requiring constant human intervention. APA agents continuously learn from new data, making them ideal for environments where rules, workflows, or priorities shift frequently.
Addressing challenges of agentic automation
While agentic automation offers significant advantages, its adoption comes with challenges that executives must navigate strategically.
- Integration Complexity: APA requires seamless connectivity with various systems, AI models, and business workflows to function optimally. A phased implementation can help reduce risks.
- Cost and ROI Justification: As with any AI-driven initiative, APA demands upfront investment. Executives should start with high-impact pilot programs that demonstrate value before scaling.
- Workforce Alignment: Involving all stakeholders, transparent communication, and training are key to ensuring APA is seen as an augmentation tool, not a replacement.
- Data Readiness and Security: APA thrives on high-quality, real-time data thus clean, structured, and accessible data is critical for success. Agentic automation includes processes involving sensitive data, as these systems become increasingly interconnected with applications and infrastructure, implementing strict security measures is a must-have.
Fostering environment for learning and experiments
Agentic automation is not a plug-and-play solution but requires an iterative approach where organizations continuously refine and optimize.
To maximize its potential:
- Encourage cross-functional collaboration between IT, operations, and business leader
- Begin with controlled pilot programs to test and refine agentic automation capabilities specific to your organization
- Measure more than just efficiency, focus on decision speed, accuracy, and business impact
Key Use Cases in Agentic Process Automation
Agentic Process Automation is transforming core business functions by enabling autonomous, context-aware decision making.
Businesses are leveraging agentic automation to drive scale operations, making them efficient, and reduce human intervention in complex workflows.
Customer Service
Agentic automation enhances customer service by automating multi-step support interactions, reducing response times, and making the engagements more personal.
- Real-time issue resolution- AI agents handle complex queries, resolve service requests, and escalate issues only when necessary.
- Dynamic sentiment analysis- AI-powered agents adjust responses based on customer sentiment, improving satisfaction.
- Proactive support and- These agents can detect issues before customers report them, triggering automated resolutions.
- Recommendations- AI agents within agentic automation analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and recommend products based on customer profile
Example: An APA agent in an e-commerce platform detects a delivery delay and
automatically notifies the customer with further information, steps, or compensation
options—no manual intervention needed.
Finance & Accounting
Finance operations involve compliance tracking, fraud detection where agentic automation can ensure accuracy and efficiency.
- Intelligent fraud detection- AI agents scan transactions in real time, identifying anomalies and flagging risks.
- Autonomous reconciliation- Matches invoices, payments, and ledger entries without manual review.
- Regulatory compliance automation- Agents adapt to policy changes, ensuring compliance without constant reconfiguration.
Example: A banking APA agent can automatically halt a high-risk transaction, verify
customer identity, and requests additional authentication before processing
Supply Chain
In supply chain and logistics, agentic automation drives real-time decision-making and dynamic planning, ensuring operations remain agile and responsive to changing conditions.
- Dynamic demand forecasting- APA analyzes market trends, supplier conditions, and inventory levels to adjust procurement strategies.
- Intelligent rerouting- AI agents redirect shipments based on real-time constraints such as weather, supplier delays, or demand surges.
- Supplier negotiations- APA evaluates contracts, benchmarks pricing, and optimizes vendor selections without human input.
IT Operations
Agentic automation introduces intelligent workflows that autonomously manage and optimize processes from technology infrastructure to support services like issue resolution, reducing downtime, etc
- Predictive maintenance- APA agents identify system failures before they happen and trigger automated fixes.
- Autonomous troubleshooting- AI-driven bots resolve common IT tickets, reducing the burden on IT teams.
- Optimized cloud resource allocation- APA dynamically scales resources based on usage patterns.
Software Development
In software engineering, agentic automation can improve productivity by automating development tasks, testing, deployment processes, etc
- Automated code generation & debugging: Suggests, optimizes, and fixes code errors in real time.
- Self-managed pipelines: AI agents can automate software testing, deployment, and rollback procedures.
- Context-aware development assistants: APA integrated into dev environments offer real-time recommendations.
Best Practices for Implementing Agentic Process Automation
- Specific goals: APA delivers best results when anchored to well-defined business objectives. The workflows should be designed to deliver measurable results.
Example: If the goal is to reduce service response time, APA agents should prioritize real-time ticket triaging, contextual responses, and automated follow-ups. - Start small to Test: Begin with a pilot program focused on a single workflow or department.
This allows teams to test APA in a controlled environment, fine-tune agent behavior, and measure real business impact before rolling it out more broadly. - Best Practice: Choose a process with clear decision points, measurable KPIs, and cross-functional collaboration like- customer support escalation or financial approvals.
- Leverage Specialized AI Agents: Design APA systems with specialized agents, each focused on a specific task or function. These agents can then collaborate across domains to improve precision and speed.
Example: In healthcare, one agent can process patient data while another handles scheduling—together they create a smoother, more efficient patient care experience. - Humans in the Loop: Despite high levels of autonomy, APA still benefits from human oversight, especially in sensitive areas.
Maintaining a human-in-the-loop model ensures AI decisions are ethical, aligned, and correctable.
Best Practice: Set up approval stages for high-impact decisions, and conduct regular audits of agent behavior. Partner with Experienced Implementation Partners: APA success often hinges on execution. Working with a partner who understands both the technology and your industry can accelerate implementation and mitigate risk.
Proper guidance helps you choose the right use cases, integrate with systems, and scale securely.
How to Implement Agentic Process Automation

Agentic Automation Trends in the Middle East
Driven by ambitious national visions, digital transformation programs, and AI-first government strategies, the region offers solid ground for agentic process automation adoption.
AI-Led National Strategies Are Enabling Adoption
Governments are creating the conditions for APA to scale UAE’s AI Strategy 2031 and Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 actively promote AI integration in government and business operations.
Public services are already using intelligent systems for identity verification, predictive service delivery, and citizen engagement—all potential APA zones.
Cross-Sector Collaboration Is Accelerating Innovation
Innovation hubs like Dubai Internet City, NEOM, and Qatar’s Free Zones Authority are connecting governments, startups, and enterprises to build automation ecosystems.
Industry Use Cases Getting Prioritized
Different industries are adopting agentic process automation to solve specific and high friction use cases
- Banking: Autonomous KYC processing, real-time fraud detection
- Retail & E-commerce: Intelligent order fulfillment, agent-led customer support
- Logistics: Shipment exception handling, warehouse orchestration
- Healthcare: Smart scheduling and triage routing in hospitals
- Energy: Predictive failure detection, remote ops control
Conclusion
Agentic process automation augments human intelligence at scale, moving the needle beyond task execution.
It doesn’t compete with your RPA or AI investments but amplifies their value by bringing them into a unified, adaptive, and outcome-driven automation strategy.
Agentic AI is one of the most transformative leaps forward for automation. As the advancements in technology happen and the adoption increases, we will see smarter decision loops.
Business chiefs in the Middle East region should act fast. National plans fueled by AI, growing corporate interest, and a nurturing environment for innovation mean those who embrace automation will be best positioned to lead the transformation, align with policy directions, and make their businesses futureproof.
Looking to implement agentic process automation in your organization, contact us for a free consultation to evaluate your business processes today.

 Dista
Dista